What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Posterior Calcaneal Spur

Overview
Heel spur is a thorn-like, bony protrusion of the heel bone, which can become inflamed through irritation, thus causing pain. A heel spur forms at the tendon attachments on the muscles of the heel bone as a result of micro-injuries to the tissue caused by overstraining. As part of the healing process for these micro-injuries, the body stores bone material in the tendon attachments as a repair mechanism. Heel spurs can develop over a very long period without causing major complaints. However, irritation of the area surrounding the ossified tendon attachment can cause inflammations. Left untreated, the inflammations can in turn lead to increased ossification and thus to permanent degradation with a risk of chronic manifestation. The normal rolling procedure that we all use when walking is then frequently no longer possible.
Causes
You are more likely to develop plantar fasciitis and heel spurs if you are Active. Sports that place excessive stress on the heel bone and attached tissue, especially if you have tight calf muscles or a stiff ankle from a previous ankle sprain, which limits ankle movement eg. running, ballet dancing and aerobics. Overweight. Carrying around extra weight increases the strain and stress on your plantar fascia. Pregnant. The weight gain and swelling associated with pregnancy can cause ligaments to become more relaxed, which can lead to mechanical problems and inflammation. On your feet. Having a job that requires a lot of walking or standing on hard surfaces ie factory workers, teachers and waitresses. Flat Feet or High Foot Arches. Changes in the arch of your foot changes the shock absorption ability and can stretch and strain the plantar fascia, which then has to absorb the additional force. Middle-Aged or Older. With ageing the arch of your foot may begin to sag - putting extra stress on the plantar fascia. Wearing shoes with poor support. Weak Foot Arch Muscles. Muscle fatigue allows your plantar fascia to overstress and cause injury. Arthritis. Some types of arthritis can cause inflammation in the tendons in the bottom of your foot, which may lead to plantar fasciitis. Diabetes. Although doctors don't know why, plantar fasciitis occurs more often in people with diabetes.
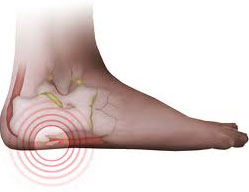
Symptoms
Bone spurs may cause sudden, severe pain when putting weight on the affected foot. Individuals may try to walk on their toes or ball of the foot to avoid painful pressure on the heel spur. This compensation during walking or running can cause additional problems in the ankle, knee, hip, or back.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will discuss your medical history and will examine your foot and heel for any deformities and inflammation (swelling, redness, heat, pain). He/she will analyze your flexibility, stability, and gait (the way you walk). Occasionally an x-ray or blood tests (to rule out diseases or infections) may be requested.
Non Surgical Treatment
There are various ways to treat heel spurs. The first is to rest and apply ice to the afflicted area. Shoe inserts and night splints can also treat plantar fasciitis, and in turn, heels spurs. Unless you have stomach sensitivities, you may want to consider taking over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medication such as naprosyn to lower the swelling. A physical therapist can recommend gentle exercises and stretches to relax the tissue around the heel bone to relieve the tension. Even with these treatments, a stubborn heel spur may not go away. A physical therapist may decide to inject cortisone into the area to decrease inflammation, but that can cause other problems such as plantar fascial rupture and fat pad atrophy. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy is also an option, which uses energy pulses to apply microtrauma around the heel spur. Surgery is also an option but is not suggested unless the heel spur lasts more than a year. To prevent heel spurs from returning, shoe inserts can relieve the pressure on the plantar fascia. Also continue the recommended stretches and exercises.
Surgical Treatment
Have surgery if no other treatments work. Before performing surgery, doctors usually give home treatments and improved footwear about a year to work. When nothing else eases the pain, here's what you need to know about surgical options. Instep plantar fasciotomy. Doctors remove part of the plantar fascia to ease pressure on the nerves in your foot. Endoscopy. This surgery performs the same function as an instep plantar fasciotomy but uses smaller incisions so that you'll heal faster. However, endoscopy has a higher rate of nerve damage, so consider this before you opt for this option. Be prepared to wear a below-the-knee walking cast to ease the pain of surgery and to speed the healing process. These casts, or "boots," usually work better than crutches to speed up your recovery time.